



Induction Hardening Machine
MALHOTRA TECHNOLOGIES offers innovative induction hardening machines designed for Increased the Hardness and durability of metal parts used induction heating processes. These machines use electrical magnetic stimulation to quickly heat metal parts, after which the metal is hardened using water or oil, which ensures improved toughness of components, wear resistance and overall durability. With robust design and modern technology.
Induction Hardening: Revolutionizing Surface Hardening Technology
Malhotra Technologies’ Induction Hardening machines are ideal for industries such as automotive, construction and aerospace where high-performance components are a requirement. These machines are known for their efficiency, energy saving and ability to process complex dimensions with a uniform intensity.
Induction Hardening is a very effective heat treatment process used to harden the surface of metal parts increase their strength and wear resistance without compromising their internal properties. This process uses electromagnetic induction to heat specific areas of work pieces. Which are then fast cooled through quenching.
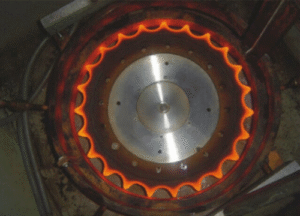
Induction Hardening Machine Example
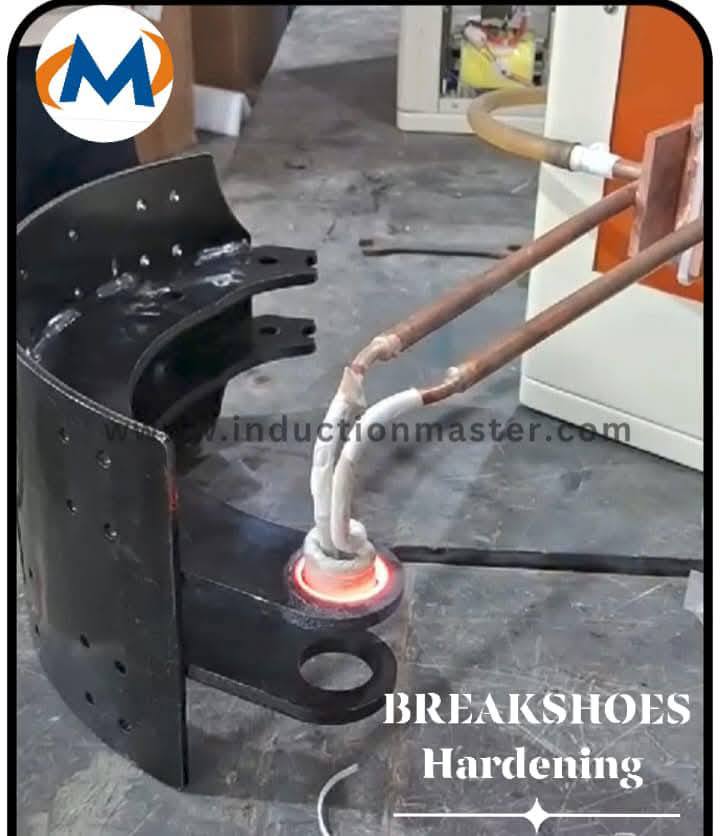








Benefits of Induction Hardening Machine
Precision and Efficiency :
Industrial as the most advantage is its Precision. To allows manufacturer target a specific area of a product. This saves Time and is more cost-effective solution.
Improved Durability :
The Hardened Surface by Induction Heating Machine provides Superior wear resistance. That is especially advantageaous such as: automotive, aerospace, hard tools, Heavy materials, and railway friction.
Localized Hardening :
Induction Hardening is Perfect for materials that only require Surface hardening. The Function to control the Depth of the Hardened area makes it perfect for Products like Gears, shafts, bearings, and Crankshafts. This Product requires a hard exterior but a softer interior for Strength and Toughness.
Environmentally Friendly :
The Induction Hardening Machine is an electrical and water-cooling system device. because it requires less energy and produces fewer emissions
Conclusion
Induction hardening machines signify a pioneering solution for surface hardening wants in few industries. With precise control, energy efficiency, and small bend, induction hardening has become the go-to choice for many manufacturers looking to improve the durability and performance of their products. even if for automotive, aerospace, or manufacturing applications, induction hardening confirms that components can hold out the toughest conditions, provided that a longer service life and superior performance.
By investing in advanced induction hardening machines, manufacturers can improve product quality, reduce operational costs, and enhance the effectiveness of their offerings.
Who Are WE
Malhotra Technologies Established in 2007, Malhotra Technologies (Induction Master) is a reputed company that manufactures and supplies a broad assortment of (INDUCTION HEATING MACHINE) induction-hardening machines, high-frequency induction heaters, medium-frequency power heaters, UHF induction heaters, annealing machine, sintering machine, electroplating rectifiers, heat-treatment machine, and brazing machine. They also supply products like 15 series induction heaters, 25 series induction heaters, 35 series induction heaters, 70 series induction heaters, medium frequency power heaters, melting machine frequency power heaters,s and forging furnace frequency power heaters. These items are developed using high-quality raw materials procured from retailers following international norms.
Frequently Asked Questions
(Benefits)
Better surface hardness and dress struggle
Increased fatigue strength
Minimal distortion compared to conventional hardening
Energy-efficient and fast process
Malhotra Technologies was founded in 2006. Malhotra Technologies is a reputed manufacturer company of induction hardening machines in India, focusing in designing and producing high-performance machines that supply to a wide range of industrial requirements. Their machines are built using the latest technology, make sure proficient and particular heat treatment of components like shafts, gears, and bearings. The company services provided advance induction heating technology, which offers fast and unbroken heating, followed by controlled cooling to improve surface hardness and uniform resistance. Malhotra Technologies efforts on providing customized results, with a strong stress on quality, consistency, and after-sales support, making them a trusted choice for manufacturers across few sectors.





